Tag: dream chaser equine auctions
Understanding Tendon Injuries in Horses: Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Tendon injuries are a common concern among horse owners and riders, often causing significant setbacks in training and performance. Tendons play a crucial role in a horse’s movement, connecting muscles to bones and providing support during locomotion. In this blog post, we will explore the anatomy of tendons and discuss different types of tendon injuries that horses may experience. Additionally, we will delve into the early signs of tendon injuries, diagnostic procedures, available treatment options, and the reasons behind the extensive recovery time associated with these injuries.
Where are a Horse’s Tendons Situated?
Tendons in horses are located throughout their bodies, but the most commonly affected tendons are in the limbs. In the lower limbs, the tendons extend from muscles in the upper leg down to the bones in the lower leg and foot. The major tendons involved in equine locomotion are the superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT), deep digital flexor tendon (DDFT), and suspensory ligament.
What Are the Different Types of Equine Tendon Injuries?
Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon Injury:
The SDFT is susceptible to overstrain and overuse injuries. These injuries commonly occur due to repetitive stress, such as intense training or sudden changes in workload.
Deep Digital Flexor Tendon Injury:
The DDFT, located behind the SDFT, can also experience strain and injuries. These injuries often result from excessive tension or severe trauma to the tendon, leading to partial or complete tears.
Suspensory Desmitis Injury:
The suspensory ligament supports the fetlock joint and can become inflamed or strained, causing suspensory desmitis. This injury can occur due to excessive strain or stress, such as landing awkwardly after a jump.
What Are the First Signs of Tendon Injury?
Early identification of tendon injuries is crucial to ensure prompt treatment and minimize long-term damage. Common signs of a tendon injury in horses include swelling, heat, pain, and lameness in the affected limb. In some cases, there may be a noticeable change in gait or a reluctance to move forward. It’s important to note that these signs may vary depending on the severity of the injury and the specific tendon affected. Horse owners and riders should pay close attention to abnormal changes in their horse’s movement or behavior.
How are Tendon Injuries Diagnosed?
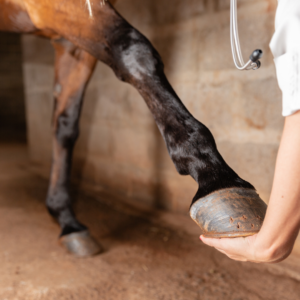 Accurate diagnosis of tendon injuries requires a thorough examination by a veterinarian. Diagnostic procedures may include palpation, ultrasound imaging, and possibly radiography. Palpation allows the veterinarian to assess the tendon’s condition, identifying any swelling, heat, or pain areas. Ultrasound imaging is a valuable tool for visualizing the tendons, enabling the veterinarian to determine the extent and location of the injury. In some cases, radiography may be necessary to rule out other potential causes of lameness.
Accurate diagnosis of tendon injuries requires a thorough examination by a veterinarian. Diagnostic procedures may include palpation, ultrasound imaging, and possibly radiography. Palpation allows the veterinarian to assess the tendon’s condition, identifying any swelling, heat, or pain areas. Ultrasound imaging is a valuable tool for visualizing the tendons, enabling the veterinarian to determine the extent and location of the injury. In some cases, radiography may be necessary to rule out other potential causes of lameness.
What Are My Treatment Options?
The treatment approach for tendon injuries in horses often depends on the severity of the injury and the specific tendon involved. Common treatment options include:
Anti-inflammatory Drugs:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain associated with tendon injuries. These medications can help manage acute symptoms and promote healing.
Physical Therapy:
Controlled exercise, including controlled hand-walking and gradually controlled turnout, can aid healing by promoting circulation and tissue repair. Rehabilitation programs may also involve cold therapy, laser therapy, far-infrared therapy, and therapeutic ultrasound.
Surgical Correction:
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the damaged tendon. Surgical techniques aim to realign torn or damaged tendon fibers, allowing for optimal healing. Surgery is typically reserved for cases not responding to conservative treatment methods.
Neurectomy:
When chronic pain persists despite conservative treatment, a neurectomy may be considered. This procedure involves selectively severing the nerves supplying the affected area to alleviate pain. However, it should be noted that neurectomy does not address the underlying tendon injury itself.
Why Does it Take So Long to Recover From a Tendon Injury?
Tendon injuries require a significant amount of time to heal due to the unique properties of tendons. Tendons have a relatively poor blood supply compared to other tissues, which means they have limited access to the oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. Additionally, the collagen fibers that makeup tendons align in a highly organized manner, making it challenging for new tissue to be laid down in the correct alignment during the healing process. This slow and meticulous healing process aims to minimize scar tissue formation and maintain the tendon’s structural integrity.
To optimize recovery, horses with tendon injuries typically require a lengthy rehabilitation period that involves controlled exercise, gradually increasing stress on the injured tendon. This controlled exercise stimulates collagen production and encourages proper tissue alignment.
Conclusion
Tendon injuries in horses can have a significant impact on their performance and well-being. Understanding the anatomy of tendons, recognizing the signs of tendon injury, and seeking prompt veterinary care is crucial for successful treatment and recovery. With proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, including anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical correction, horses can regain their mobility and return to their previous level of activity. Although the recovery process can be lengthy, it is essential to prioritize the long-term health and well-being of the horse to ensure a successful return to full function.
 The American Quarter Horse is a breed that has become an integral part of American history. It is a versatile horse breed known for its speed, strength, and agility. The breed’s origin can be traced back to colonial America when Spanish explorers brought horses to the new world. The horses were a cross between the Spanish Barb and the native horses of the American continent.
The American Quarter Horse is a breed that has become an integral part of American history. It is a versatile horse breed known for its speed, strength, and agility. The breed’s origin can be traced back to colonial America when Spanish explorers brought horses to the new world. The horses were a cross between the Spanish Barb and the native horses of the American continent.